FUNCTION AND
CONSTRAINTS |
MAXIMIZE1 |
MINIMIZE1 |
Thermal insulation,
transitional |
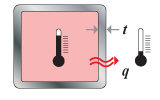 |
optimize thermal
stability; temperature difference, time fixed; thickness free |
1 / a = ρ Cp / λ |
a = λ / ρ Cp |
Thermal insulation,
cyclic heating |
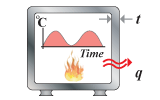 |
optimize energy
consumption per cycle; temperature rise, cycle time fixed; wall
thickness free |
(√a) / λ =
(λρCp)-1/2 |
λ / (√a) =
(λρCp)1/2 |
| optimize mass;
temperature rise, cycle time, wall thickness fixed |
(√a) / λ =
((ρCp)/λ)1/2 |
λ / (√a) =
(λ/(ρCp))1/2 |
Thermal insulation,
steady state |
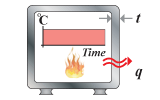 |
optimize mass;
minimum heat flux at steady state; thickness specified |
ρ / λ |
λ / ρ |
Heat exchanger
tubes |
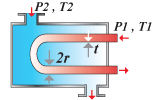 |
maximum heat
flux per unit area; no failure under Δp |
λ σy |
1 / λ σy |
| optimize mass;
maximum heat flux per unit mass; pressure and temperature difference,
tube radius fixed; wall thickness free |
σy2λ / ρ |
ρ / σy2λ |
Short-term thermal
energy storage |
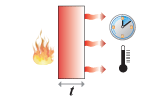 |
optimize energy
stored for given temperature rise and time |
λ / (√a) =
(λρCp)1/2 |
(√a) / λ =
1 / (λρCp)1/2 |
| maximize energy
stored for given temperature rise and time |
1 / (ρ√a) =
(Cp/λρ)1/2 |
ρ√a =
(λρ/Cp)1/2 |
Long-term thermal
energy storage |
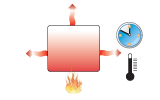 |
maximum energy
stored / unit material cost (storage heaters) |
Cp / Cm |
Cm / Cp |
Thermal stability |
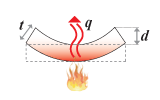 |
minimize thermal
distortion for given heat flux |
λ / α |
α / λ |
Thermal shock
resistance |
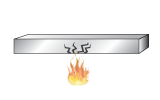 |
maximum change
in surface temperature; no failure |
σy / Eα |
E α / σy |
Heat sinks |
|
maximum heat
flux per unit volume; expansion limited |
λ / Δα |
Δα / λ |
| maximum heat
flux per unit mass; expansion limited |
λ / ρ Δα |
ρ Δα / λ |







